Authoritative Guide to Virtual Studio
What is a virtual studio?
The virtual studio system uses camera tracking technology to obtain real shot data, which is combined with a background image generated by a computer-controlled LED display. The background image or video played by the LED display screen is controlled by the computer, which can be changed rapidly according to the needs of the studio, which makes the colorful studio scene design can be realized by very economical means.
The content displayed on the LED display is exactly the same as the three-dimensional perspective relationship of real people, which can avoid unreal and unnatural viewing experience and make the audience feel that this is the real scene. Due to the infinite charm of the virtual studio itself and its development prospects that cannot be underestimated, it has been paid attention to by more and more TV station program production and professional film production companies and applied to the actual shooting work.
Virtual studio is a brand-new tool for producing TV programs and movie content. Virtual studio technology includes camera tracking technology, LED display virtual scene presentation, chroma key technology, lighting technology, etc. The virtual studio technology is based on the traditional chroma keying technology, making full use of the computer 3D graphics technology and video synthesis technology, according to the position and parameters of the camera, so that the perspective relationship of the 3D virtual scene is consistent with the foreground content.
After chroma key synthesis, the host in the foreground looks completely immersed in the three-dimensional virtual scene generated by the computer and can move in it, thereby creating a very real and three-dimensional TV studio effect.
Using virtual studio technology, any imaginary scene and props can be created. Whether it is static or dynamic, whether it is real or virtual. This only depends on the designer’s imagination and the level of 3D software designers. Many effects that cannot be achieved in real studios can be easily achieved in virtual studios.
For example, skyscrapers are set up in studios, hosts are doing “live” broadcasts from the moon, tornadoes are blowing in the studio, and so on. You may not have noticed that some TV stations have now used virtual hosts. They can not only host programs with real hosts, but also host programs independently. These are all disruptive effects created by virtual studio technology.
Advantages Of Virtual Studio
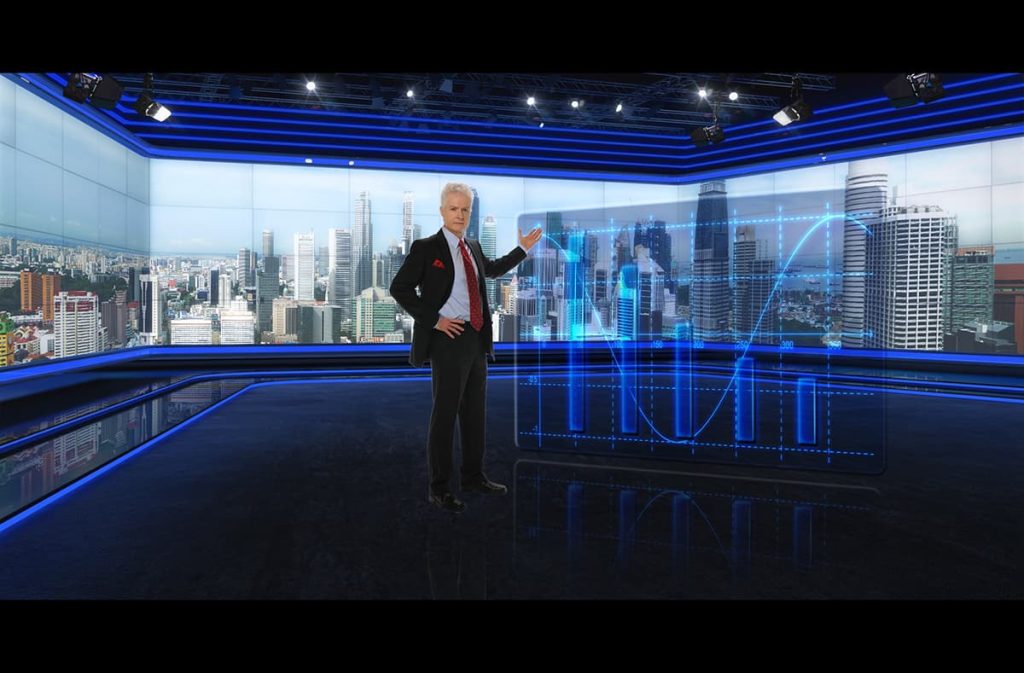

1. The background of building a virtual studio is generated by computer and can change rapidly, which makes colorful studio scene design can be realized by very economical means.
2. The virtual studio system can display important text, pictures, animation, and video data on the virtual large-screen video wall or any scene props in real time, making the column more vivid.
3. Using the virtual studio system to produce programs can not only complete the three-dimensional synthesis of the program host and the three-dimensional scene props in real time, but also play video content, animation, real-time subtitles, lines, etc. on multiple windows of any shape or on the surface of any object. It can be fully adapted to the time length and rhythm of the content explained by the program host, so that the program shooting, editing and post-processing can be completed in real time at one time.
4. The visual experience of the virtual studio system, such as real-time virtual special effects, real-time virtual lighting, real-time environment projection, real-time ground mirroring, real-time fogging, and real-time synthesis of internal and external scenes, makes the program creation more attractive.
Technical Analysis of Virtual Studio
Camera tracking and positioning
Determining camera status information is critical during virtual studio programming. The number of dedicated digital cameras for virtual studios is usually two to three, and the cameras are equipped with motion detection and recognition systems, namely camera trackers. There are two tracking methods: optical recognition system and mechanical sensing system. The principle is to transmit the detected motion data of the camera’s sensing parts such as pushing, pulling, shaking, moving, focusing, zooming and even lifting to the “calibrator” through a “sensor” device. The “virtual” cameras in the virtual studio are relatively locked in one position. When the live studio camera moves, the virtual camera is controlled by the tracker to synchronize with the live camera in real time.

Position lock for virtual camera
Another important and unique problem with virtual studios is the positional relationship between cameras. The virtual camera is not directly related to the initial position of the real camera. It can be placed anywhere in the virtual space. When there are more than two cameras in the studio for switching, the positions of the actual actors and scenes in the virtual studio must remain unchanged. , that is, the relationship with the virtual scene remains unchanged. Otherwise, when switching, the audience will see the actor jumping from one place to another in the background, creating a visually unrealistic effect. Since the real object and the actor are given by the real camera, and the background is given by the virtual camera, the position of the virtual camera must be locked, that is, the distance between the virtual cameras must be equal to the distance between the real cameras, and the push-pull, panning The initial amount (in-position vector) of , is consistent with the position and direction relationship of the real camera before switching can be performed.
Natural switching of zoom focus depth of field
In actual shooting, the focus point of the camera generally tracks the host. If the foreground and background are clearly focused at this time, an unnatural sense of depth of field will occur. Especially in close-up shots, the background should be out of focus, so that the foreground and the background seem to come from the same camera, otherwise, this kind of virtual studio is unsuccessful. In order to solve this problem, when the camera tracks the changes of the host or actor’s body movements, the content displayed in the LED display screen is blurred or clearly processed through the background switching mode preset by the computer. Such zoom, focus and depth of field transformation operations need to be matched with dedicated virtual background processing software to achieve the effect of a real simulated picture. The virtual studio display screen and the corresponding full screen content processing system provided by GalaxyAV are able to handle these technical problems perfectly, so that the audience can hardly notice that this is a virtual background content presented by the LED display screen.

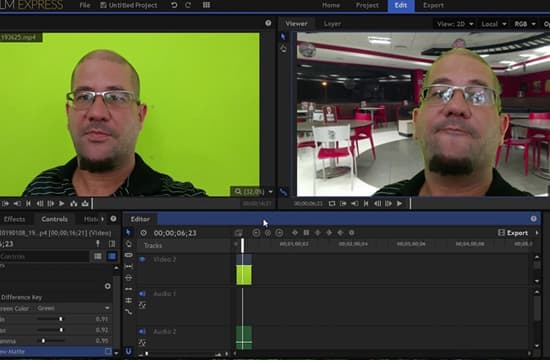
Chroma key and blue box arrangement and processing
Chroma key (keying), the blue box mainly has three processing methods: one wall and one bottom, two walls and one bottom (one corner), and three walls and one bottom. Among them, the three-wall and one-bottom type can give more space, the camera position limit is small, and the panning range is large. The blue box must ensure a uniform blue background, especially in the wall-to-wall and wall-to-ground junctions, there should be no traces of seams. At the same time, due to the use of chroma key technology in the production process of the program, the shadows cast by actors and real props in the blue room must also enter the virtual space together with the actors and props, and the shadows of characters and environmental scenes under the studio lighting will be cut out. , creating a sense of unreality. Due to the use of chroma key technology, a delay will occur, which not only requires the system to increase the foreground video delay unit, but also must consider other issues. One is sound. Since the foreground video is delayed, in order to ensure the synchronization of sound and picture, a video frame synchronizer needs to be added.
Integrated computer technology comprehensive processing system
The computer equipped in the virtual studio system is a small computer network, and the host is the network center, which is the control center of the virtual studio and the “director’s desk” for the production of the virtual studio program. In addition to calling and adjusting the pre-made three-dimensional virtual scene, it is also responsible for transmitting image data to the graphics generator and processing the camera motion data transmitted by the camera tracker. The motion of the virtual three-dimensional computer scene is calculated in real time according to the camera motion data sent from the host, so as to ensure that the output virtual background is synchronized with the real foreground.
An important task in the preparation of a virtual program is to create a three-dimensional model. The background image of the virtual studio can be a live video from a video recorder or a camera, or a still image, etc., but the most used two-dimensional or three-dimensional model CG (Computer Graphics) created by a computer, that is, a virtual scene. Although the background of the virtual studio can be changed infinitely in principle, the creative work of the background and 3D modeling are quite complicated. It is no longer a good system that can be fully used by one or two people. It requires directors, creators, artists, etc. Collaboration between designers, 2D modelers, 3D modelers, actors, and operators of virtual systems.


Track and trackless virtual studio shooting technology
Orbital virtual studio shooting technology uses optical or mechanical sensor tracking devices to track and calculate the position and movement of real cameras, and generate data streams for transmission to the system host. The data is calculated and analyzed by the system host, so as to realize the movement of the real camera in the blue box of the same proportion, and reflect the different changes of the depth of field in the 3D scene. The most popular image manipulation method is to use a chroma keyer to replace a blue or green background with a live scene.
Trackless virtual studio shooting technology does not need to use sensors to track and calculate the position and movement of the camera. Trackless virtual studio adopts virtual scene positioning technology to realize the seamless combination of virtual camera movement and 3D scene in real time. By driving the virtual camera, the push-pull, panning, rocker, aerial photography and other motion effects of each camera position are realized, as well as the fast switching between each camera position.
The formulation of the virtual scene shooting plan
The director’s ideas are made into a detailed “storybook” by the art designer. The so-called detail refers to how each picture element moves, how the host’s position changes, and whether there are close-up shots in the virtual scene. Because the lens is advanced, it means that the computer-generated image is enlarged. This must require that the size of the image generated in advance be large enough to advance the lens without causing the pixel to become larger. The particularity of the virtual studio operation requires the director to communicate with the producer of the computer animation scene in advance on the details of each shot so that the producers responsible for implementing the script plan can fully understand the director’s intention and prepare the 3D scene well in advance.

Why we can provide you with the perfect virtual studio solution?
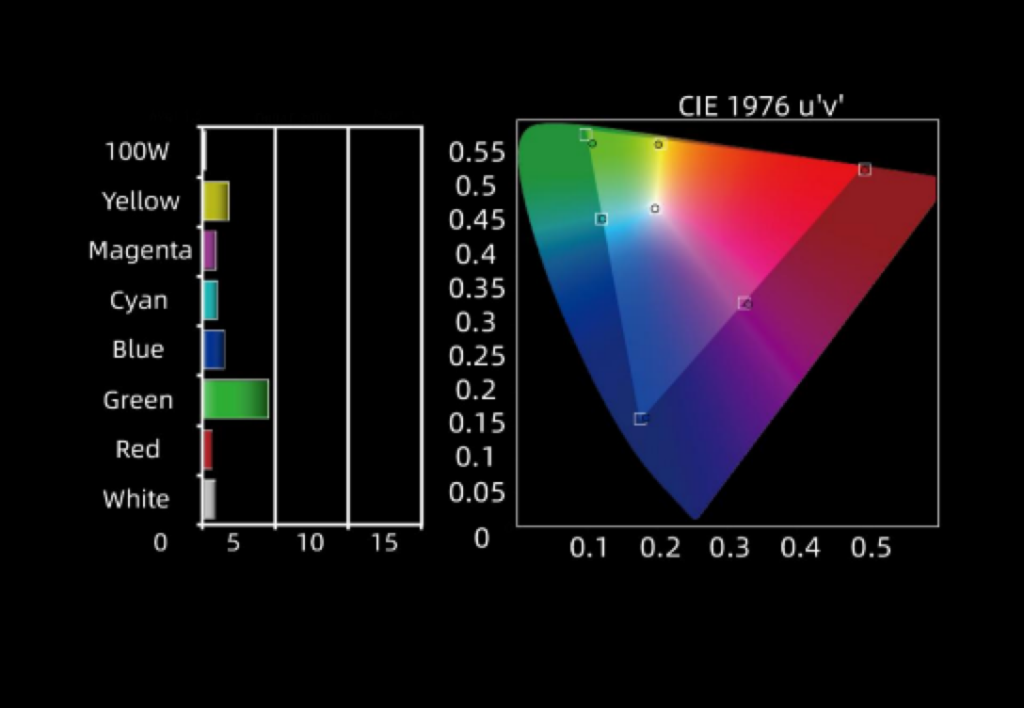
Color Space
GalaxyAV pick up the center part of high quality wafer to produce the unique LED chips which can emit the most pure RGB lights. In this way, we can infinitely approach the nature color range that humans can see. Galaxyavi has got the goal at 100% DCI-P3 and 85% Rec. 2020.
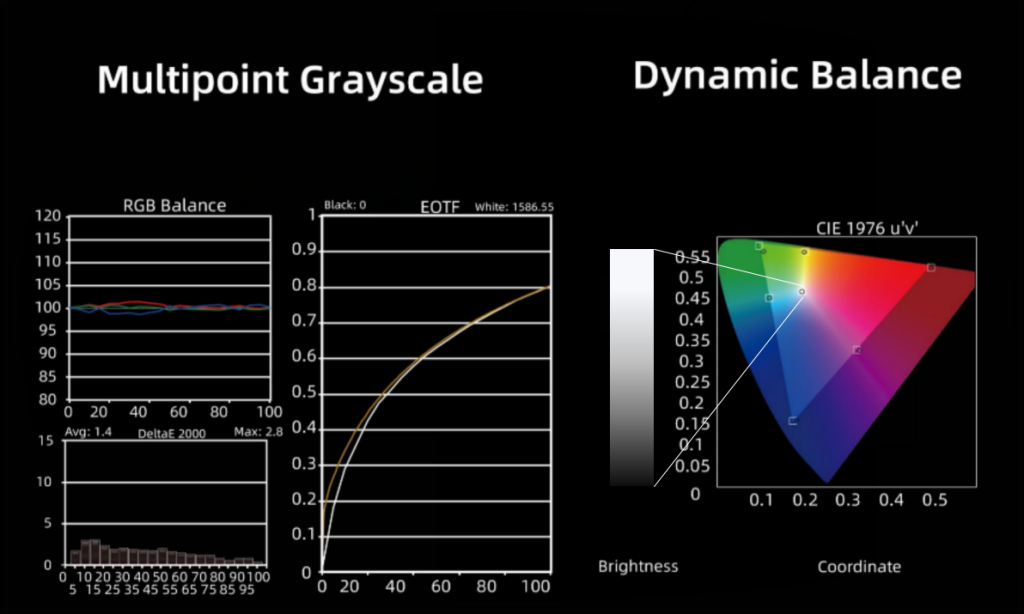
Dynamic Balance
We took an uncompromising approach to develop an intelligently designed LED video wall solution that eliminates the major pain points of traditional LED technology from installation to maintenance and servcing to operation, Micro Tiles LED works smarter so you don’t have to.

Support frame multiplexing
Utilize low scan technology High frame rate up to 240Hz. To meet the filmmakers’ high efficient shoot work, one shoot but multi contents. It provides more possibilities for future film work.
Color Gamut:90% REC2020; 110% DCI-P3
Micro LEDS is another step towards more realistic Images. Galaxyavi team is always going after in color:” Redder” reds, “greener” greens, “bluer” blues, brighter and more. In the place you will enjoy richer, more lifelike colors than you’ve ever seen.


Moire-effect off
4-IN-1 LED and special surface process technology help reduce the Moire-effect.
High Brightness
GalaxyAV virtual studio LED brightness up to 2000nits. Meet the clients’ requirement for film-making.
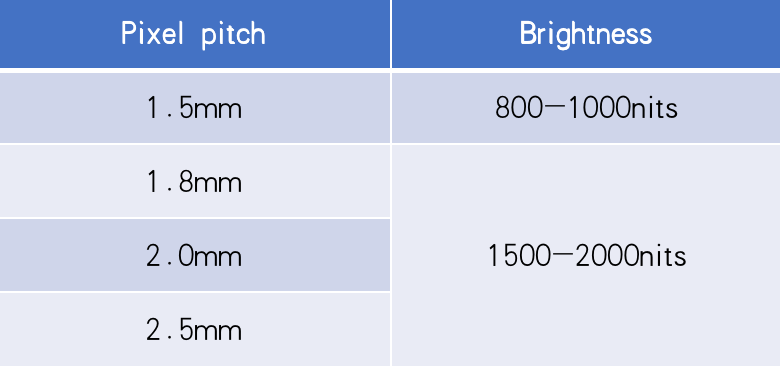
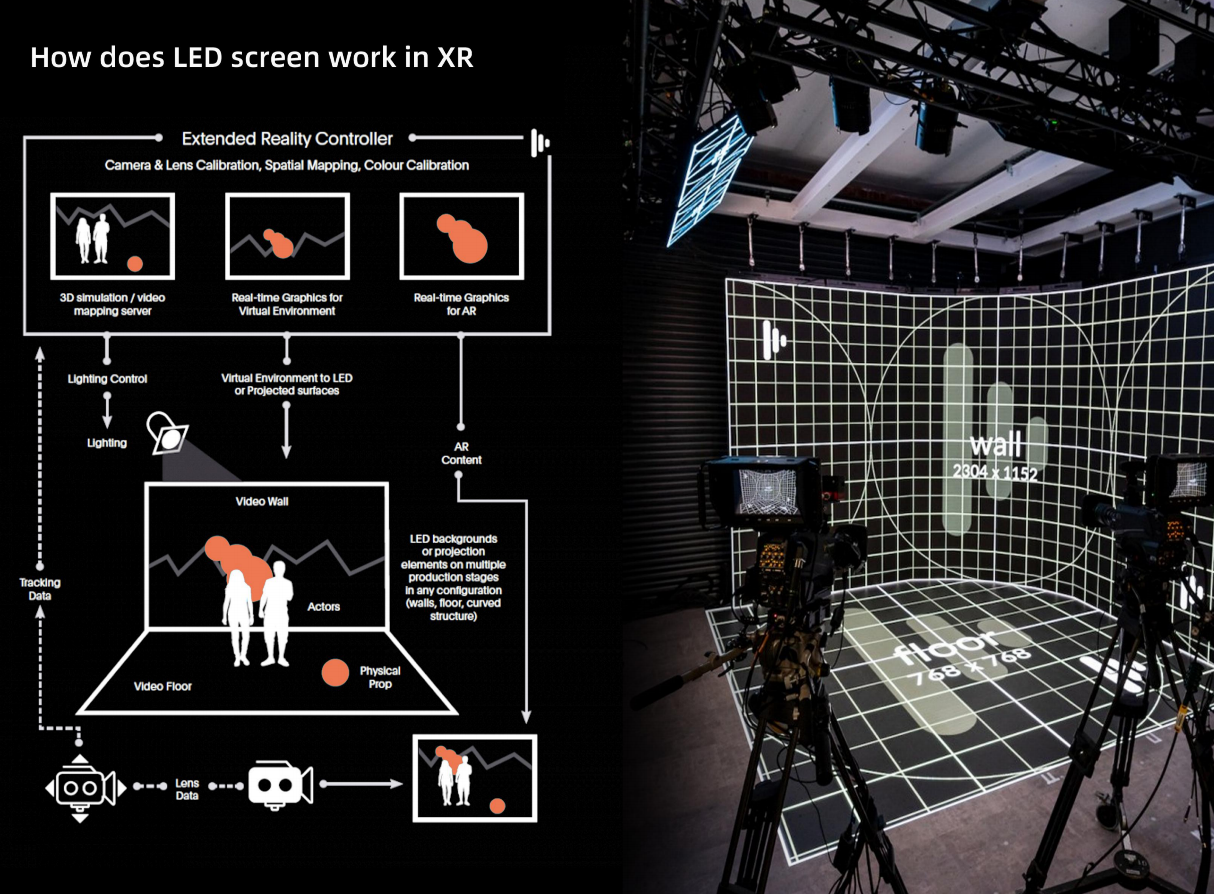
How does GalaxyAV LED display screen work in virtual studio?